- By TOP CHINA FREIGHT
- August 6, 2025
- Shipping
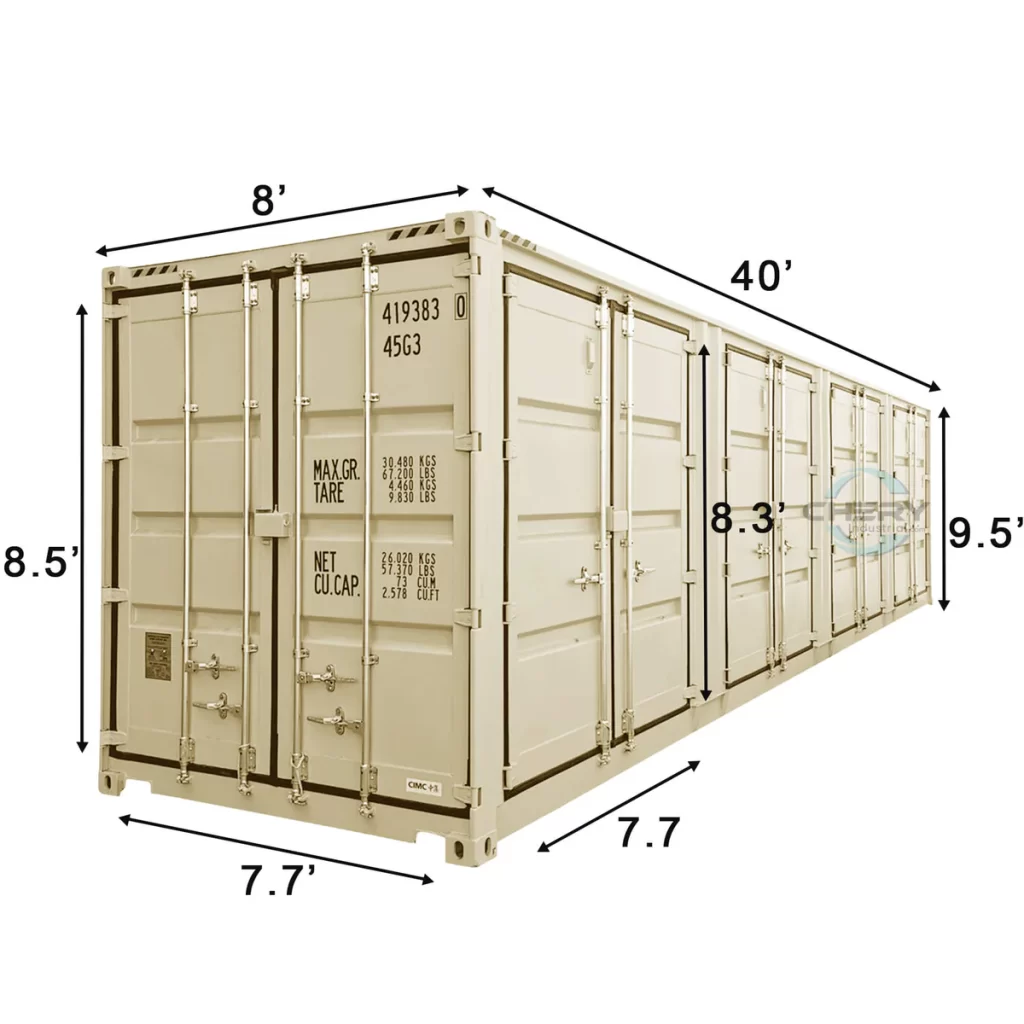
1.What Is a 40' High Cube (HQ) Container?
A 40’ HQ container is a type of dry cargo shipping container that measures 40 feet in length and features an additional foot (about 30 cm) of internal height compared to standard 40-foot containers.
That extra space allows for greater internal volume, making it ideal for:
- Voluminous yet relatively light cargo (e.g. textiles, plastic goods)
- Stacking multiple pallet layers
- Shipping awkwardly shaped or tall items
2.Dimensions & Capacity of a 40’ HQ Container
| Specification | Measurement (Metric) | Measurement (Imperial) |
|---|---|---|
| External Length | 12.19 m | 40 ft |
| External Width | 2.44 m | 8 ft |
| External Height | 2.896 m | 9 ft 6 in |
| Internal Length | 12.03 m | 39 ft 5 in |
| Internal Width | 2.35 m | 7 ft 8 in |
| Internal Height | 2.69 m | 8 ft 10 in |
| Door Height | 2.58 m | 8 ft 6 in |
| Volume | ~76.3 cubic meters | ~2,694 cubic feet |
3.40' HQ Container Weight Limit (kg)
Here’s where the keyword “40′ hq container weight limit kg” comes into play. Shipping a 40’ HQ container involves understanding three key weight measurements:
- Approximate: 3,800 – 3,950 kg
- This is the weight of the empty container itself.
- Standard Limit: 30,480 kg
- This is the maximum total weight the container can carry, including its tare weight and the cargo inside.
Typical Range: 26,500 – 28,600 kg, depending on the tare weight and the shipping line’s policy.
However, local road, rail, and port regulations may further reduce this limit. Always check with your freight forwarder or carrier before loading.
4.Real-World Use: How Weight Limits Affect Shipping
Understanding the 40’ HQ container weight limit (kg) is crucial for the following reasons:
1. Compliance with International Regulations
Most global shipping lines and carriers follow ISO standards that cap container weights to ensure safety during handling, stacking, and transit.
2. Avoid Overweight Penalties
Exceeding the declared weight limit may result in:
- Customs delays
- Fines or fees
- Shipment rejection
- Mandatory unloading or repacking
3. Road Transport Restrictions
In countries like the United States, road weight limits (e.g., federal and state axle weight limits) may reduce how much you can legally move inland—even if the container is under the ocean freight limit.
4. Verified Gross Mass (VGM)
Under SOLAS regulations, shippers are legally required to declare the Verified Gross Mass of a container before it is loaded onto a vessel. This includes both:
- Cargo weight
- Container tare weight
Failing to declare an accurate VGM can result in shipping delays or container rejection.
5.Ideal Cargo for 40’ HQ Containers
Due to their larger internal space, 40′ HQ containers are commonly used for:
- Furniture & home goods
- Electronics and appliances
- Automotive parts
- Machinery and equipment
- Stackable palletized items
- Consumer goods in large volume
Shippers often maximize volume rather than maxing out the weight—especially when transporting lightweight but space-consuming items.
6.Summary Table: 40’ HQ Container Weight Specs
| Weight Metric | Approximate Value (kg) |
|---|---|
| Tare Weight | 3,800 – 3,950 kg |
| Max Gross Weight | 30,480 kg |
| Max Payload Capacity | 26,500 – 28,600 kg |
Always confirm with your carrier for route-specific limitations.
7.Pro Tips for Shippers
1.Check the CSC plate on the container to verify its exact tare and MGW values.
2.Use load planning software to ensure weight is evenly distributed across the container.
3.Weigh your cargo using certified scales before submission of VGM.
4.Consult your freight forwarder about local transport laws and weight limits by country or region.
5.Label heavy cargo clearly to help handlers avoid container floor damage or injury.
Conclusion
Understanding the 40′ HQ container weight limit in kg is essential for any business involved in international shipping. Always verify the tare weight of the container,the maximum gross weightand the weight capacity permitted by local regulations and the shipping line.By planning accordingly, you avoid costly mistakes and ensure a smoother, more efficient supply chain.
Ask for a quote
Whether you’re shipping commercial goods, oversized items, or full container loads, our team can help you.
Contact us today and get a fast, no-obligation quote tailored to your cargo type, destination, and schedule.
FAQs
Q1:How do I calculate the maximum cargo weight I can load?
Use this simple formula:
Max Gross Weight – Tare Weight = Max Payload
For example:
30,480 kg – 3,900 kg = 26,580 kg (maximum cargo you can load)
Q2:Is the weight limit the same in all countries?
Not always. While ISO container limits are standard, road and rail regulations vary by country. For example, U.S. truck weight limits may require reducing container load to avoid exceeding axle weight laws.
Q3:What happens if I overload a 40' HQ container?
Overloading can result in:
- Fines or overweight surcharges
- Shipment delays or rejection at port
- Legal violations (especially in road transport)
- Risk of container damage or collapse
Q4: What does "tare weight" mean?
Tare weight is the weight of the empty container, typically 3,800–3,950 kg for a 40’ HQ container. This must be subtracted from the total allowed gross weight to determine how much cargo can be safely loaded.
Q5:Can I reduce the tare weight by using a different type of container?
Some newer or specialized containers (like aluminum high cubes) may have slightly lower tare weights, giving you a higher net payload. Check with your freight forwarder or container supplier.
