- By TOP CHINA FREIGHT
- September 22, 2025
- Sea Freight, Shipping
Table of Contents
For businesses importing goods, understanding ocean freight rates China is essential to control costs and maintain supply chain efficiency. Shipping expenses can make or break profitability, especially when container prices fluctuate. This guide provides a detailed look at costs, transit times, and strategies to help you secure the best rates for your shipments.

What are current ocean freight rates from China?
Ocean freight rates vary by destination, container size, and season. In 2025, average costs for a 20ft container range from $900–$1,300, while a 40ft container typically costs $1,600–$2,600.
| Container Size | Average Rate (USD) | Capacity (CBM) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20ft Container | $900 – $1,300 | 28–30 CBM | Small bulk shipments |
| 40ft Container | $1,600 – $2,600 | 58–60 CBM | Large, heavy cargo |
| 40ft HC | $1,700 – $2,800 | 68 CBM | High-volume cargo |
| LCL (per CBM) | $35 – $60 | Shared space | Low-volume shipments |
Moreover, rates are influenced by demand, fuel surcharges, and carrier capacity. Importers must check updated prices regularly, as even small shifts affect overall budgets.
Why do ocean freight rates from China fluctuate?
Costs rise before Chinese New Year and Western holidays.
Increases in bunker fuel impact shipping line surcharges.
Blank sailings and capacity limits affect supply.
Delays at major ports like Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Ningbo add extra fees.
Tariffs and customs changes can increase costs.
How does sea freight compare to air and rail?
Ocean freight is the most cost-effective method for large shipments, but slower than alternatives. Here’s a comparison:
| Mode of Transport | Avg. Cost | Transit Time | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea Freight | $900–$2,600/container | 30–40 days | Cheapest per unit, high capacity | Slow, weather delays |
| Rail Freight | $4,000–$6,000/container | 18–25 days | Faster than sea, eco-friendly | Higher cost, limited routes |
| Air Freight | $6–$12/kg | 5–7 days | Fastest, reliable | Expensive, limited size |
Additionally, importers often combine sea freight with inland trucking to balance cost and speed.
What is the average transit time for ocean freight from China?
Transit time depends on destination port and route.
| Destination Port | Average Transit Time |
|---|---|
| UK (Felixstowe) | 30–35 days |
| USA (Los Angeles) | 18–22 days |
| USA (New York) | 30–35 days |
| Australia (Sydney) | 20–25 days |
| Europe (Hamburg) | 28–32 days |
Therefore, businesses should account for at least one month of lead time when planning ocean shipments from China.
What documents are required for ocean freight shipments?

Shipping without the right documents can lead to customs delays and added costs.
| Document | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Bill of Lading (B/L) | Proof of shipment |
| Commercial Invoice | Declares value and description |
| Packing List | Confirms weight and dimensions |
| Certificate of Origin | Identifies production country |
| Import Declaration | Required by customs |
| HS Codes | Determines tariff and duty rates |
How do container types affect freight rates?
Container selection impacts cost efficiency.
20ft container
Ideal for smaller loads, lower upfront cost.
40ft container
More space, better per-unit cost for larger shipments.
40ft HC (High Cube)
Extra height provides more capacity, suitable for bulky cargo.
Reefer container
Specialized for temperature-controlled goods, higher cost.
Moreover, choosing the right container prevents paying for unused space or costly adjustments.
How can importers reduce ocean freight costs from China?
Reserve space weeks ahead to secure lower rates.
Use LCL to combine goods with others.
Experienced forwarders access better rates.
Reduce wasted space for maximum efficiency.
Shipping during off-peak periods lowers costs.
Case Study: Apparel Importer Saving on Ocean Freight

A UK apparel company imported 3,000 cartons of clothing from Ningbo to London. The options were:
- Air Freight – $9/kg, $28,000 total, 6 days transit.
- Sea Freight (40ft container) – $2,200 total, 33 days transit.
- Rail Freight – $5,200 total, 21 days transit.
Decision:
The company selected sea freight, saving over $25,000 while meeting store delivery schedules.
Lesson:
For non-urgent, high-volume shipments, sea freight delivers the best value.
Should small businesses use LCL shipments?
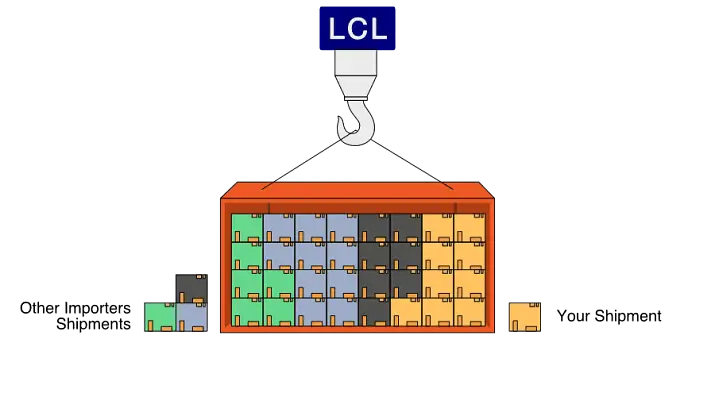
Yes, Less than Container Load (LCL) is ideal for businesses with smaller volumes.
Advantages of LCL:
- Lower upfront cost.
- Flexibility for testing markets.
- Efficient for irregular shipments.
Disadvantages of LCL:
- Longer handling time.
- Higher risk of delays due to consolidation.
- More handling increases minor damage risk.
Therefore, LCL helps small importers remain competitive without overpaying.
What hidden charges should businesses expect?
Even with competitive rates, hidden charges can increase total cost:
- Port handling and documentation fees.
- Demurrage charges for delayed container pickup.
- Customs duties and VAT.
- Delivery fees from port to warehouse.
- Insurance for high-value cargo.
Therefore, always request a full cost breakdown from forwarders before booking.
Conclusion
Managing ocean freight rates China requires balancing cost, speed, and reliability. Sea freight remains the most economical choice for large shipments, while air and rail serve urgent or mid-volume needs. Importers can reduce costs through early booking, consolidation, and proper documentation. By understanding rate fluctuations, hidden charges, and container choices, businesses can keep supply chains efficient and profitable.
Need a Shipping Quote?
If you want expert guidance and peace of mind, our team is ready to assist.
TJ China Freight offers tailored solutions to help businesses of all sizes ship more reliably from China.

FAQ
Q1:What is the average cost of ocean freight from China?
A 20ft container costs $900–$1,300, while a 40ft container ranges from $1,600–$2,600.
Q2:How long does ocean freight from China usually take?
Transit times range from 20–40 days depending on the destination port.
Q3:Can I ship small quantities without a full container?
Yes, LCL shipping allows you to share container space and pay per cubic meter.
Q4:Do I need insurance for ocean freight shipments?
Yes, insurance protects against damage, loss, or theft during sea transit.
Q5:Which factors influence ocean freight rates most?
Fuel prices, seasonal demand, carrier capacity, and port congestion.
