- By TOP CHINA FREIGHT
- September 11, 2024
- Service, Shipping
China is Canada’s second-largest trading partner, significantly impacting the Canadian economy. Key imports from China include electrical machinery, furniture, textiles, and plastic products. If you’re considering importing from China, this guide will help you navigate the process from obtaining permits to calculating costs.
Obtaining Import Licenses and Permits in Canada
Before importing goods into Canada, businesses or individuals must obtain a Business Number (BN) from the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA). This import/export account is free and can be obtained quickly.
Certain products may require additional permits or certificates, managed by the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA).
Canadian Customs Declaration
All commercial imports are subject to customs duty and Goods and Services Tax (GST), unless exempt. Importers must convert the value of goods into Canadian dollars to calculate duties. Canada’s de minimis thresholds are C$40 for taxes and C$150 for duties. Goods below these thresholds are exempt from duties and taxes.
Classifying Your Goods
Canada uses the Harmonized System (HS) for classification, aligned with international standards. The system includes a 6-digit international code and an additional 4-digit Canadian-specific code to determine duty rates.
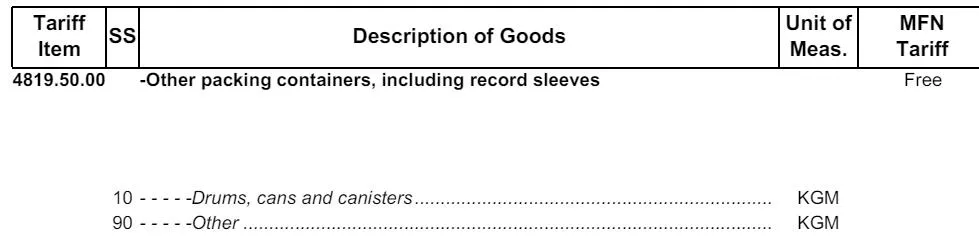
Tariff Classification Example
| Tariff Classification Number | Details |
|---|---|
| 4819.50.00.90 | |
| Heading (International) | 4819 |
| Sub-heading (International) | 4819.50 |
| Tariff Item (Canadian) | 4819.50.00 |
| Statistical Suffix (Canadian) | 4819.50.00.90 |
Calculating Duties and Taxes
Use the classification number to find the applicable duty rate under Canada’s Customs Tariff Schedule. For example, if you import goods valued at US$1,000 with a 4% duty rate and a 5% GST:
| Calculation | Amount |
|---|---|
| Value in CAD | US$1,000 x 1.2 = C$1,200 |
| Customs Duty (4%) | C$1,200 x 4% = C$48 |
| Total for GST Calculation | C$1,200 + C$48 = C$1,248 |
| GST (5%) | C$1,248 x 5% = C$62.4 |
| Total Duties & Taxes | C$110.4 |
Importers with a positive compliance record face fewer customs delays and may benefit from special release options.
Shipping Methods to Canada
Sea Freight
Sea freight is a cost-effective option for shipping goods to Canada, available in Full Container Loads (FCL) or Less-than-Container Loads (LCL). Major Canadian ports include:
| Port | Location |
|---|---|
| Vancouver | British Columbia |
| Montreal | Quebec |
| Prince Rupert | British Columbia |
| Halifax | Nova Scotia |
Transit times for sea shipments from China typically range from 20 to 40 days.
Air Freight
Air freight is faster but more expensive than sea freight. Major Canadian cargo airports include:
| IATA Code | Airport Name | City |
|---|---|---|
| YYZ | Lester B. Pearson International Airport | Toronto |
| YUL | Montreal / Pierre Elliott Trudeau Intl | Montreal |
| YVR | Vancouver International Airport | Vancouver |
Direct flights from China to Canada take about 12 hours, but total transit time can be up to 10 days, depending on customs and handling.
Courier Services
For smaller shipments (under one cubic meter or 200 kg), express couriers like DHL, FedEx, and UPS are ideal. Canada applies a CAN$20 threshold, above which customs fees may apply.
How TCF Can Assist You
TCF offers comprehensive shipping services, including sea, air, and courier options. We help you navigate customs processes, optimize routes, and provide cost-effective solutions tailored to your needs. Contact us for a quote and start your importing journey with confidence today!
